What is Electricity Voltage Current and Resistance – Complete 2025 Beginner’s Guide

📝 Introduction
⚡ What is Electricity Voltage Current and Resistance – Ultimate 2025 Beginner’s Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Electricity?
- What is Voltage?
- What is Current?
- What is Resistance?
- How They Work Together
- Understanding Ohm’s Law
- Real-Life Examples
- Conclusion
🔌 Introduction
What is electricity voltage current and resistance — this is one of the most essential questions anyone entering the world of electronics must ask. These four terms form the foundation of every electrical system. Whether you’re powering a smartphone, lighting up your room, or building a robot, electricity and its core concepts play a vital role.
In this post, we’ll break down each of these ideas using real-life examples, analogies, and beginner-friendly explanations.
⚡ What is Electricity?
Electricity is the flow of electric charge, typically carried by electrons moving through a conductor like a copper wire. It is the energy that powers everything from tiny microchips to massive power grids.
Electricity is invisible, but we see its effects in our everyday life — lighting, heating, motion, and communication.
🔋 What is Voltage?
Voltage is the electric potential difference between two points. In simpler terms, it’s the “pressure” that pushes electric charges through a wire.
Imagine a water tank: the higher the water level, the more pressure it has. Similarly, higher voltage means more electrical “push.”
- Unit: Volt (V)
- Symbol: V
- Example: A AA battery has 1.5V; a wall socket has 220V or 110V depending on your country.
🔗 External link: Energy.gov – Voltage Basics
🔄 What is Current?
Current is the rate at which electric charge flows. It tells us how many electrons are moving through the circuit in a given time.
Think of current as the flow of water in a pipe. The more water (electrons) flowing per second, the higher the current.
- Unit: Ampere (A)
- Symbol: I
- Example: A phone charger may provide 2A of current.
🧱 What is Resistance?
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of current in an electrical circuit. Every conductor has some resistance, and it converts electrical energy into heat.
Imagine a narrow water pipe: it resists flow more than a wide one. That’s resistance in action.
- Unit: Ohm (Ω)
- Symbol: R
- Example: A 100-ohm resistor limits current flow in electronic circuits.
⚙️ How They Work Together
Let’s compare electricity to a plumbing system:
| Electrical Term | Water Analogy |
|---|---|
| Voltage | Water Pressure |
| Current | Flow Rate |
| Resistance | Pipe Size |
When you increase the voltage (pressure), more current flows. But if resistance (pipe size) increases, the current decreases.
This relationship is governed by Ohm’s Law.
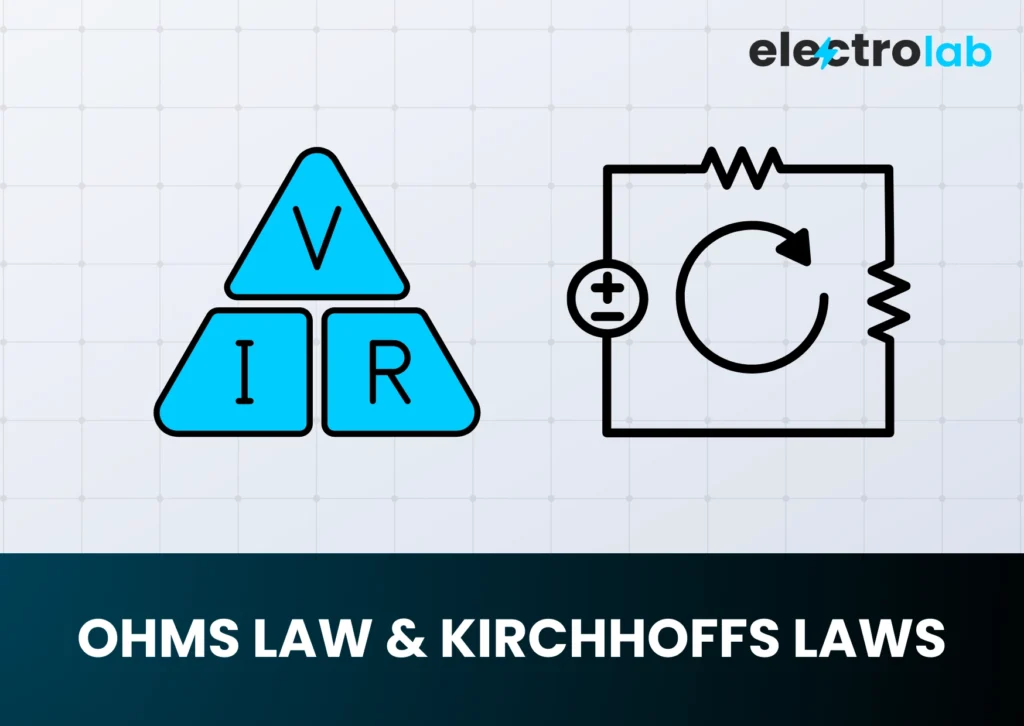
📏 Understanding Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law is the golden formula for calculating the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
Formula:
V = I × R
Where:
- V = Voltage
- I = Current
- R = Resistance
From this, you can also derive:
- I = V / R
- R = V / I
This simple formula is used in every field of electronics.
💡 Real-Life Examples
Here are some practical uses of electricity voltage current and resistance:
- LED Bulb
- Voltage: 220V AC
- Current: 0.05A
- Resistance limits the brightness and protects the LED.
- Mobile Charger
- Voltage: 5V
- Current: 2A
- The charger uses a resistor to control output.
- Electric Heater
- High resistance wire heats up when current flows, converting electricity into heat.
🔗 Internal link: Explore DIY Electronic Projects on Electrolab
🖼️ Image
Alt: What is electricity voltage current and resistance – Ohm’s Law chart

✅ Conclusion
So, what is electricity voltage current and resistance? In simple terms:
- Electricity is the flow of charge
- Voltage is the push
- Current is the flow
- Resistance is the opposition
These four concepts work together to power everything around us. From lighting a bulb to charging your phone, understanding these basics is essential for anyone interested in science, technology, or engineering.